Globalization makes the food system even more complex with multiple suppliers and companies involved. However, that has created a challenge in maintaining food security even where laws and policies have been published. The frequent occurrences of food scandals have reduced consumers’ trust in the food industry. The food safety issues arise due to operational mistakes, including contamination, mislabeling, undeclared ingredient, biological causes, etc.
Some of the most well-known food scandals in history are the China 2008 Sanlu milk scandal, the Germany 2011 Enterohemorrhagic E.coli outbreak due to contaminated fenugreek sprouts, Europe 2013 horse meat scandal – a food labelling fraud, the US 2017 multi-state Salmonella outbreak of Maradol papayas, the 2017 contaminated egg scandal in Switzerland, Hong Kong, and EU-15 states and the US 2018 outbreak of E. coli of Romaine lettuce.
Tragically, more food poisoning outbreaks reported in 2019 – 2020. For instance, an outbreak of Salmonella Newport illness that was linked to frozen ground tuna in America, Salmonella–infected British eggs, the Netherlands Listeria monocytogenes infected meat. Ultimately, these incidents raised food safety concerns among consumers which changed their buying behaviour.
Therefore, all the stakeholders should share the responsibility of food security, including food producers, food retailers, related governments, and customers. Supply chain management is playing a significant role in addressing food insecurity and contribute to food recall and public health. All these can be accomplished through technological innovations for efficient traceability system.
The digitalization of the supply chain can achieve strategic improvements for agri-food companies. Most recently, blockchain has drawn significant attention that could revolutionize society to solve food traceability issues.
This article looks into presenting what is blockchain technology, how it can be important and beneficial for the agri-food industry. Also, the application of blockchain technology in the food industry.
What is Blockchain Technology?
The blockchain technology was developed to innovate financial transactions using Bitcoins, as currency exchange and cheap reliable global payment system. It bypasses the traditional financial intermediaries like banks.
Blockchain technology is a record-keeping distributed database of shared public ledgers, a more efficient way to record and exchange information. Whereby, no single person, or a company, or a government, or an entity, owns the data.
Blockchain is an expanding list of records, called blocks linked by cryptography. Each block contains a data set, timestamp, cryptographic hash (cybersecurity fingerprint) and the hash of the previous block. By design, a blockchain is resistant to alteration of the data. The infographic below illustrates how blockchain works:
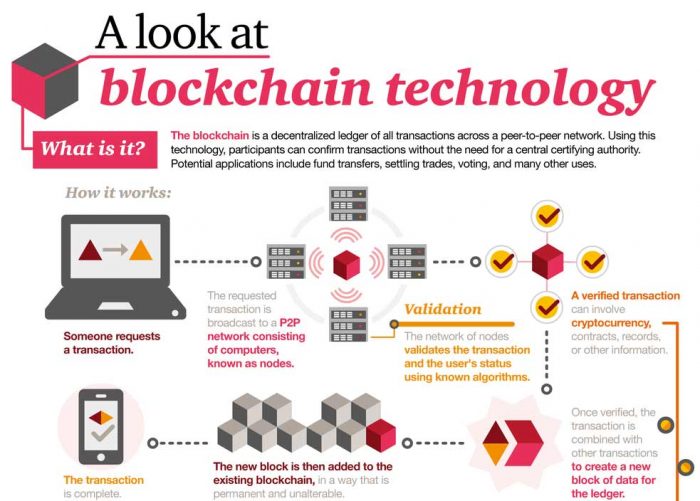
Source: Gary Fox
The 4 Main Attributes of Blockchain Technology
1. Decentralization
Allows authorized users to have the same power to upload and check information. Unlike traditional transactions that need to be approved by central authorities. Thus, blockchain eliminates the central powers and addresses information inequality by allowing for a direct transaction between the users.
2.Security
Prevents break down of the whole network because a single point failure will not lead to the failure of the whole network, which can minimize the chance of hacking.
3. Immutability
Ensures the records’ originality and authenticity. Meaning that historic data cannot be modified without notifying other users. Hence, this can reduce the human intervention on records.
4. Smart contract
A digitalized contract and operates automatically once pre-established conditions are met. This can fasten the transactions and improve trust. No single users can make changes on contract as it is based on the agreement of all members in the network.
Also Read: How Blockchain can help Small and Medium Enterprises?
Importance of Blockchain Technology in The Food Industry
Now, why would blockchain, a technology originally developed for financial management and cryptocurrencies, be important for the food industry?
When compared to other industries, the value chains of the food industry are more vulnerable. It requires more attention to production, post-harvest handling, processing, transportation, marketing, distribution and retailing especially when dealing with the seasonal and time-sensitive products.
On top of it, food has a natural characteristic of changing in quality constantly. Furthermore, external environments such as temperature and shipping can change food products’ quality and freshness. Besides that, processed food with a longer shelf life might involve complicated production process with a mixture of many ingredients. Those complications contribute to higher risks of product failure and need to be extra careful with the quality of raw material. So, these are the major challenges the food industry facing today where blockchain technology can be a promising solution.
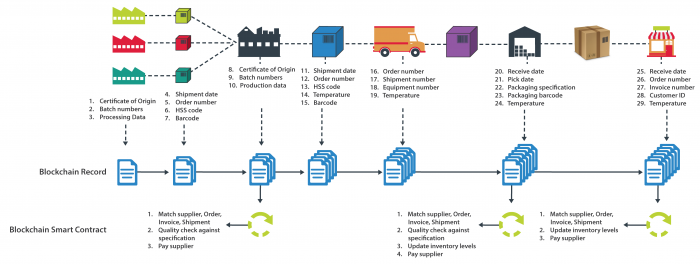
Blockchain technology guarantees the traceability and authenticity of information that would impact the food supply chain dramatically. Furthermore, smart contractual relationships create a trusted environment such as enforcing product authenticity certification and ownership certification of suppliers. The certificates are permanently registered along the chain. Thus, the technology controls the risk of supply chain members moving fraudulent foods.
IDC predicted by 2021, about 30% of manufacturers and retailers globally will have built digital trust through blockchain services. So, that enable collaborative supply chains and allow consumers to access product histories as well as reduces transaction costs by 35%.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology in The Food Industry
1. Strengthen Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can improve transparency, security, and robustness of the food supply chain. The technology provides a shared information platform for all partners in the supply chain. It verifies the origin of food products or raw materials, real-time location, and status of the product at any step to monitor inventory and quality standard along the supply chain. In addition, it gathers detailed information such as product temperature, environmental conditions and other important factors for quality management purposes, which is particularly important for perishable products.
Most importantly, it secures the collected records as it reduces the risks of data stealing and hacking. As a result, blockchain technology helping companies to create a more informed and predictable supply chain as well as they gain 360 views of entire supply chain activities.
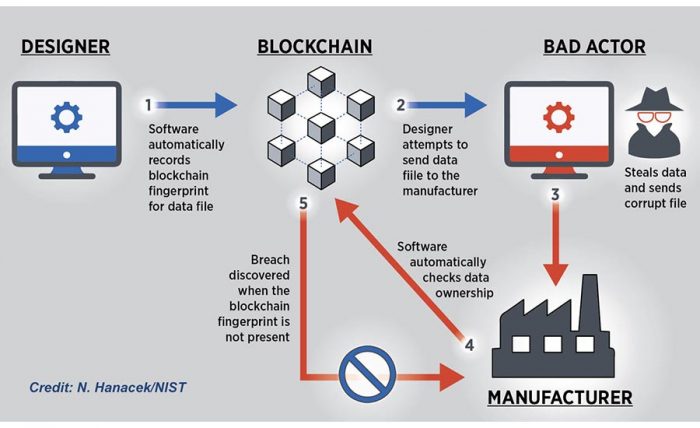
2. Mitigate food fraud while protecting the brand
Data on a blockchain is permanently stored and maintained by all stakeholders within the supply chain network. Blockchain’s biggest importance is in providing traceability for everyone on the chain – from farmers through manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers and consumers. Multiple stakeholders can have direct product profile access, save the copies of records, also can be retrieved on-demand anytime. For instance, manufacturers can monitor their suppliers to make sure that raw material quality meets requirements. Whereas, the end-users, consumers can trace the product’s journey to determine its origin and guarantee their authenticity.
Meanwhile, the full transparency of data helps brand owners to quickly and proactively identify the source of contamination. So, they can manage potentially harmful food fraud without disrupting the whole supply chain.
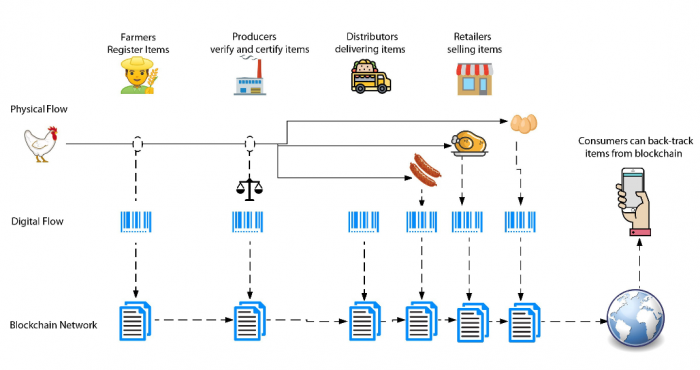
3. Built trust and loyalty of consumers
A blockchain-based supply chain builds trust amongst supply chain stakeholders in the way food products are manufactured, processed and delivered. Because the data uploaded visible to anyone within the network that is error-free, cannot be manipulated or hacked. Thus, this brings transparency and trust to the complex supply chain. It protects every stakeholder’s benefits and eliminates information inequality.
Blockchain helps boost consumer confidence with automatic digitizing and easily sharing audits, certificates, and other relevant records on sustainable practices. It also acts as evidence for containing products, such as halal food, organic food, fair trade food, etc. So, consumers will assume better quality, which will increase their purchasing decision power.
4. Food supervision
According to the WHO, almost 1 in 10 people globally suffer illness due to eating contaminated food globally, resulting in 420 000 deaths of which 125 000 are children under 5 years old. Fortunately, a blockchain-technology eliminates counterfeit products along the food supply chain. Blockchain can notify foodborne outbreaks. Also, it analyzes the root cause of the outbreaks since the food market transaction information is already been recorded. Subsequently, the number of disease outbreaks and victims can be reduced. Moreover, Immutability feature of blockchain is specifically useful during food recall, which can prevent any related stakeholders to change history and escape from responsibilities.
5. Prevents price coercion
Blockchain technology applications in the food industry reduce transaction fees and middlemen or intermediaries. Consequently, intermediates would get less chance to collect more money from farmers or manufactures. So, food producers can reap better and significant economic benefits. Plus, the consumer gets the premium quality products delivered by brands with a good reputation at reasonable prices.
6. Prevents food wastage
According to the United Nations’ Food and Agriculture Organization, around 1.3 billion tons which are approximately one-third of food produced in the world gets wasted yearly.
By blockchain-based traceability, it is possible to track the quantity of food wasted and food rescued throughout the entire supply chain. Thus, this leading to reduced product loss and increased margins. Moreover, the stakeholders can regulate the operation of the supply chain in a charitable manner as they can arrange food aid for families struggling with hunger and malnutrition.
Notably, untargeted food recall is one of the major causes of food wastage. Blockchain technology can improve food recall efficiency. You can retrieve needed information, isolate products from certain suppliers, and narrow down the products recall range. It can help to remove certain products and ingredients from the root of the problem immediately to prevent further loss.
On the other hand, Food Marketing Institute and the Grocery Manufacturers Association revealed that a company’s average cost of a food recall is $10M – in addition to brand damage and lost sales according to a joint industry.
7. Sustainability
Food companies are encouraged to be more sustainable as the traceability feature of blockchain able to monitor environmental impacts. The traditional traceability system mainly depends upon paper-based systems and cause difficulties for stakeholders’ integration. Moreover, paper documentation can be time-consuming and cause human errors. Yet, blockchain’s smart contract can save paperwork, minimize human labour efforts and reduce unnecessary costs. For instance, the payment can be transferred to producers automatically once the products arrive at the warehouse.
Furthermore, the global supply chains become more complex with diverse policies to adapt in different countries. Globalized standardization can be adaptable for all countries by applying blockchain. So, companies can avoid duplicative works as well as can save resources and time.
8. Integration with Enterprise resource planning (ERP) and Internet of things (IoT)
Integrating ERP, IoT with blockchain technology can be highly beneficial. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) streamlines inventory and production management processes includes trade, logistics, delivery, warehousing information. While, IoT is an intelligent and high-speed information network that connects physical products through sensor includes GPS, GIS, RFID, WSN, etc.
IoT devices capture accurate and real-time data in a continuous stream that can automatically feed into the internal ERP systems. Thus, no more manual recording or no human effort required to scan a barcode. This real-time information capturing ability is particularly important for frozen and fresh food products, as the quality is closely related to the external environment.
The synergy between ERP, IoT and blockchain foster the exchange of immutable data along the supply chain and the smart contracts accelerate processing time. Analysis of massive quantities of reliable data leads to the right decisions. So, you can transform your operations from a reactive to a proactive approach.
Application of Blockchain technology in The Food Industry
Some prominent organizations have cooperated blockchain technology and enhanced their supply chains organizationally and technologically such as:
1. Walmart
Walmart collaborated with Chinese retailer JD.com, and Tsinghua University to handle product safety issues in food supply chains in China. Besides that, they are tracing over 25 products such as fresh fruits, leafy greens, dairy, meat, poultry from different suppliers. Beyond tracking the origin of products, Walmart aims to address food safety issues by identifying the source of a foodborne disease outbreak. Walmart will be coordinating more effective recalls of foods potentially contaminated. Moreover, it’s considering storing additional data to facilitate sustainable practices in the supply chain.
2. JD.com
JD.com China’s second-biggest online shopping has made it possible for customers to look at a detailed history of their steaks – from when the cow was born to what it was eating before it’s served on their dinner tables.
3. Barilla
Barilla is using blockchain technology to guarantee the origin and quality of Italian fresh basil for its pesto.
4. Nestle and Carrefour
Nestle and Carrefour track baby milk products and provide consumers with data on their origins and movements “from dairy to shelf.” Customers will be able to scan a QR code on the milk’s packaging to access a range of information.
In addition, Carrefour also allows consumers to scan the QR Code on a product’s label such as organic chickens and Sicilian oranges and lemons to access information on their smartphone.
Most recently, Nestlé has announced that it will be expanding its use of blockchain technology to trace their luxury coffee brand Zoégas. Consumers can simply scan the QR code on the packaging and follow the coffee journey – from the growing locations to the Zoégas factory where the beans are roasted, grounded and packed. The data includes information about farmers, time of harvest, transaction certificate for the specific shipments, as well as the roasting period.
5. Alibaba
Alibaba has launched an initiative called “Food Trust Framework” which allows Chinese customers of Tmall Global (Alibaba-owned marketplace) to monitor shipments of food from Australia and New Zealand.
6. World Wildlife Fund (WWF)
The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) in Australia, Fiji and New Zealand, in partnership with high-tech, tuna fishing and processing companies, has launched a pilot project in the Pacific Islands tuna industry that will use blockchain technology to fight against illegal tuna fishing and to certify the origin of tuna through a QR Code.
Final words
By applying blockchain technology, companies in the food supply chain can communicate transparently to consumers and regulators. Moreover, it raises awareness about sustainability opportunities and practices at each step of the supply chain. Substantively, blockchain technology improves brand equity, reputation, and trustful relationships with consumers.
“Blockchain is driving a new breed of enterprise applications that could drastically improve cooperation for wholesale distribution. The blockchain-based solution from SAP provides the best opportunity to fully satisfy our need to be interoperable with our trading partners and their solutions as well as to remain compliant with the U.S. DSCSA.”
– Jeffery Denton, senior director, Global Secure Supply Chain, AmerisourceBergen Corporation.
“Blockchain holds incredible promise in delivering the transparency that is needed to help promote food safety across the whole supply chain”
– Bridget van Kralingen, senior vice president at IBM Industry Platforms.













